Does DE Diatomaceous Earth work on Mold / Dust Mite YouTube
How to Use Diatomaceous Earth in Potted Plants

These properties make it useful as a filter media, an absorbent, and as a lightweight filler for rubber, paint, and plastics. When diatomite is crushed into a powder, it is usually called "diatomaceous earth," or D.E. Diatoms are microscopic, single-celled algae that live in marine or fresh water. They produce hard parts made of silicon dioxide.
The Wonderful Uses of Diatomaceous Earth Infographic Guide DENutrients Diatomaceous Earth

How does diatomaceous earth work? Diatomaceous earth is not poisonous; it does not have to be eaten in order to be effective. Diatomaceous earth causes insects to dry out and die by absorbing the oils and fats from the cuticle of the insect's exoskeleton. Its sharp edges are abrasive, speeding up the process.
6 Proven Diatomaceous Earth Uses and Benefits Dr. Axe

diatomaceous earth, light-coloured, porous, and friable sedimentary rock that is composed of the siliceous shells of diatoms, unicellular aquatic plants of microscopic size. It occurs in earthy beds that somewhat resemble chalk, but it is much lighter than chalk and will not effervesce in acid. Under a high-powered microscope the form of the diatoms can be distinguished.
5 Health Benefits Of Diatomaceous Earth

Diatomaceous earth (often abbreviated D.E.) comes from a soft sedimentary rock deposits called "Diatomite". It is a soft very fine grained rock, rich in silica that is composed of the remains of fossilized diatoms. Deposits of diatomite are found all over the earth and range in color from white (very pure) to buff, grey and occasionally black.
Diatomaceous Earth Uses For Humans Idalias Salon

A sample of food-grade diatomaceous earth Scanning electron micrograph of diatomaceous earth. Diatomaceous earth (/ ˌ d aɪ. ə t ə ˈ m eɪ ʃ ə s / DY-ə-tə-MAY-shəs), diatomite (/ d aɪ ˈ æ t ə m aɪ t / dy-AT-ə-myte), celite or kieselgur/kieselguhr is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous sedimentary rock that can be crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a.
Diatomaceous Earth.

Diatomaceous earth is not poisonous; it does not have to be eaten in order to be effective. Diatomaceous earth causes insects to dry out and die by absorbing the oils and fats from the cuticle of the insect's exoskeleton.. Also, it does not emit vapors or dissolve well in water. The ocean contains vast amounts of diatomaceous earth. Many.
The Many Health Benefits of Diatomaceous Earth I Breathe I'm Hungry
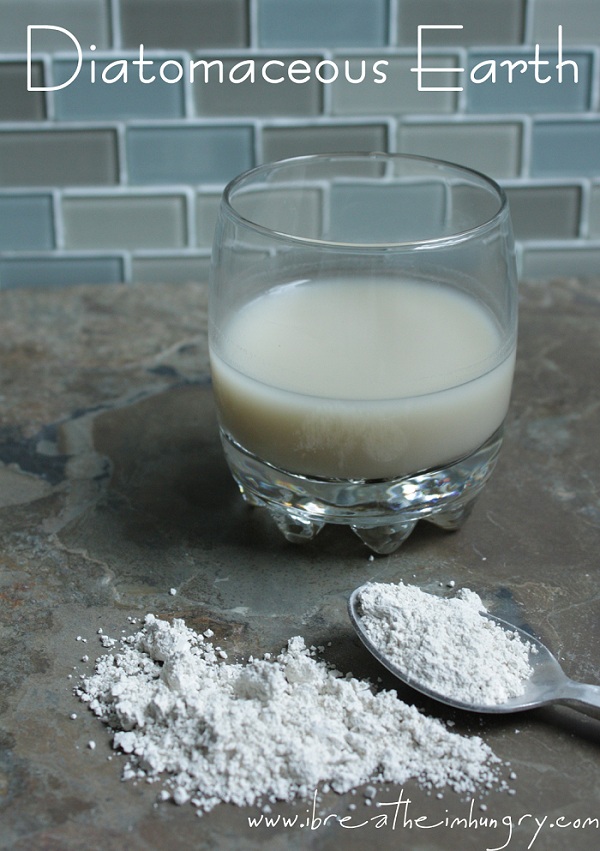

Diatomaceous earth is taken orally by mixing the powder with water and drinking the liquid. It must be taken right away because the powder doesn't actually dissolve in water . Anecdotal reports suggest starting with a teaspoon of diatomaceous earth and gradually working up to a full tablespoon, but reliable advice backed by nutrition experts.
Uses for Diatomaceous Earth What is it? Diatomaceous Earth is a soft powder formed

Diatomaceous earth doesn't work after it gets wet since water causes DE to wash away and lose its sharpness, making it less potent. When DE particles dry, whatever's left of them regain their effectiveness, but for maximum impact against garden pests, DE must always be reapplied after it gets wet. DE is one of those products that's.
12 Proven Food Grade Diatomaceous Earth Benefits And Uses

Diatoms dissolve in an alkaline solution, notably at pH>9, forming silicic acid. This solution may however not be very stable. Cite. Johan Macuer. Universidad Católica del norte, Coquimbo. Muchas.
Diatomaceous Earth Also Known As Diatomite Mixed in Glass of Water. Stock Photo Image of

Diatom filter. Diatomaceous earth (DE) filtration is a special filtration process that removes particles from liquids as it passes through a layer of fossilized remains of microscopic water organism called diatoms. These diatoms are mined from diatomite deposits which are located along the Earth's surface as they have accumulated in sediment of.
Diatomaceous Earth capsules, DE, food grade, silicarich, water sourced, fossil shell flour

Diatomaceous Earth (DE) filtration is a process that uses diatoms or diatomaceous earth—the skeletal remains of small, single-celled organisms—as the filter media. DE filtration relies upon a layer of diatomaceous earth placed on a filter element or septum and is frequently referred to as pre-coat filtration.
DE (diatomaceous earth) Water Chemistry Austin Reef Club

The Wet Method. The easiest way to apply diatomaceous earth wet is to mix the powder with water. The best ratio is mixing four tablespoons of diatomaceous earth with an entire gallon of water until the powder completely disintegrates. The water will then have a somewhat sticky texture but will continue to be a liquid.
How To Use Diatomaceous Earth Garden & Home Pest Brigade

2. Mix 4 tablespoons (59 ml) of diatomaceous earth with 1 gallon (3.8 L) of water. Use a water jug, bucket, or similar container to hold the contents. Pour in 4 tablespoons (59 ml) of diatomaceous earth for every gallon (3.8 L) of water. Mix these together thoroughly until the powder dissolves.
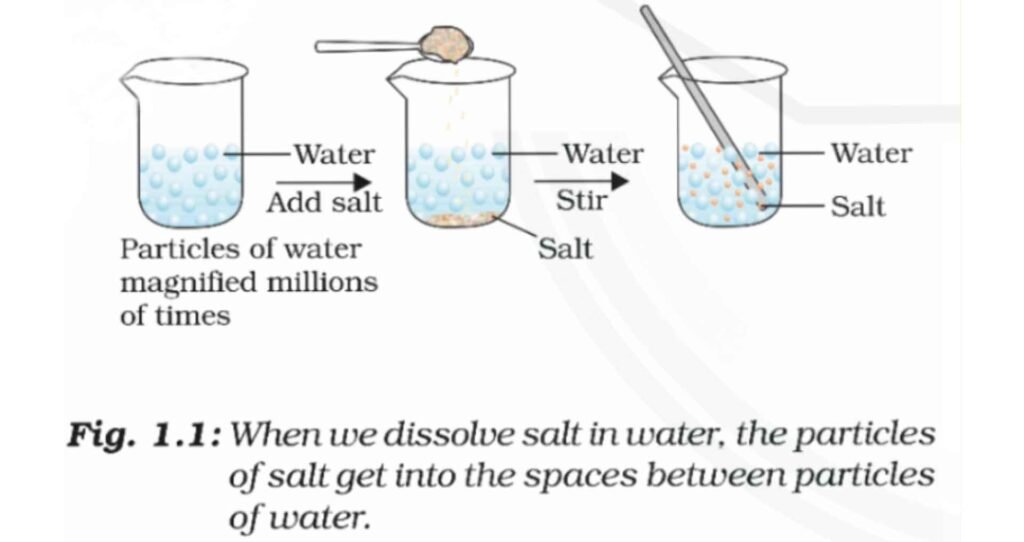
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 1 Eduvik
DE mixed with water is commonly known as a slurry. To make a DE slurry, follow this ratio: ½ cup DE (8 tablespoons) for 2 cups of water. You can apply the slurry with a spray bottle or a pressure washer. Once you mix the DE in the water, the DE will settle to the bottom, so you need to shake it up frequently as you spray.
★Diatomaceous Earth Health Benefits and Side Effects Food Grade Diatomaceous Earth★ YouTube

1. DIATOMACEOUS EARTH Diatomaceous earth - also known as DE, diatomite, diatomaceous silica, kieselguhr and infusorial earth - is actually a non-metallic mineral composed of the skeletal remains of microscopic single-celled aquatic algae called diatoms. Diatomaceous earth as it naturally occurs is predominantly composed of
Diatomaceous Earth Powder and in Water Stock Photo Image of diatoms, rock 143288002

Diatomaceous earth ( DE) is the fossilized skeletons of microscopic single-celled aquatic organisms called diatoms. Their skeletons are made of a natural substance called silica—which makes up 26% of the Earth's crust by weight. Deep deposits of diatomaceous earth are mined in the western United States in places where lakes once covered the.
.